EUMETCast Satellite Acquisition Station Contatto S.Laviola
Two data and image acquisition systems based on the multi-service dissemination system EUMETCast are active in Bologna and Roma laboratories. The stations are operational 24/7 for the acquisition of data from Meteosat and from geostationary and polar satellites of EUMETSAT, NOAA and other space agencies (e.g., EPS, GOES-E/W, MTSAT, FY2, MODIS). The data acquisition and archival allow the Group to participate to national and international projects that require the usage of data from meteorological and environmental satellite sensors. The data are both Level 1 (multichannel imagery) and Level 2, that is meteorological products (instability indexes, wind vectors, cloud classification maps, precipitation intensity, etc…).
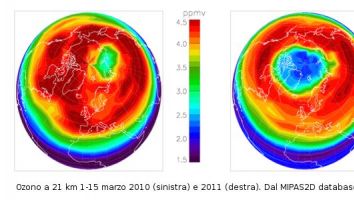
Remote Sensing of the Stratosphere contatto B.Dinelli
Several resources are available at ISAC-Bologna and ISAC-Rome facilities for the analysis of remote sensing measurements, acquired in the Earth stratosphere and on other solar system planetary atmospheres. They also consist in some calculators ( one with 7 Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3770 CPU @3.40GHz processors) used for the analysis of remote sensing measurements and for the storage of the obtained results, e.g. database of vertical temperature, pressure and VMR (Volume Mixing Ratio) profiles of stratospheric constituents - MIPAS2D database, link). The atmospheric composition is obtained through the use of algorithms for the analysis of remote sensing measurements from aircraft and satellite platforms. Those algorithms have been used to obtain Earth atmospheric composition (e.g. analysis of Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS)/ENVISAT measurements) and for the analysis of atmospheric composition of other planets, such as the Titan's high atmosphere (from VIMS/Cassini measurements). In the future they will contribute to the study of transport of disequilibrium species in Giovian hot spots and H3+ ions concentration from their auroral emissions. This last objective will be reached through the analysis of measurements from the JIRAM (Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper, PI Alberto Adriani INAF-IAPS, realized by Selex-Galileo), the infrared image spectrometer onboard JUNO mission - link. MIPAS2D database: http://www.isac.cnr.it/~rss/mipas2d.htm e http://www.mbf.fci.unibo.it/index.html JUNO/JIRAM: http://solarsystem.iaps.inaf.it/jiram/about-jiram/