Snowfall over the ice-free ocean: what we can learn from the latest frontiers researches
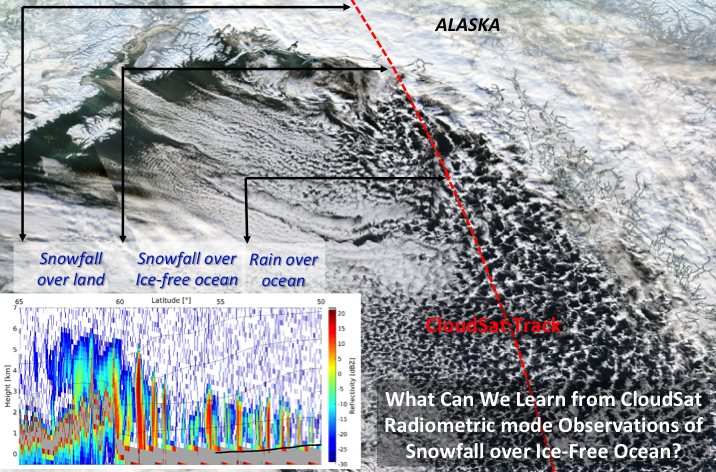
The CloudSat 94 GHz radar provides the most complete snowfall climatology over polar regions, but accurate quantitative snowfall estimates derived from radar reflectivity (figure in the preview) remain challenging. The published work  explores the value of the CloudSat 94 GHz Brightness Temperature, a novel product developed from the processing of the radar noise floor level, combined with path-integrated attenuation, a standard product derived from the reduction in the radar surface return.
Special Issue "Remote Sensing of Water Cycle ECVs and their Applications"

The focus of this Remote Sensing of the Water Cycle Special Issue is on remote sensing-related Essential Climate Variable - Climate Data Records (ECV-CDRs) of all water cycle components and their applications. Submitted manuscripts will preferably report scientific advances in the following topics, but other topics related to the scope of the SI will also be considered:
SPECIAL ISSUE “REMOTE SENSING OF THE WATER CYCLE IN MOUNTAIN REGIONS”

The Guest editor Elisa Palazzi (CNR-ISAC), together with the colleague Joerg Bendix of the University of Marburg, announces the Special Issue “Remote Sensing of the Water Cycle in Mountain Regions” of Remote Sensing (ISSN 2072-4292, IF 4.118).
Special Issue "New Insights into Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate"

The Guest editor Pierina Ieplo (CNR-ISAC) announces the Special Issue "New Insights into Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate" of Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417) belonging to the section "Environmental and Sustainable Science and Technology".
The topics of interest for this Special Issue include, but are not limited to the following:
