Amazzonia: la deforestazione riduce le piogge
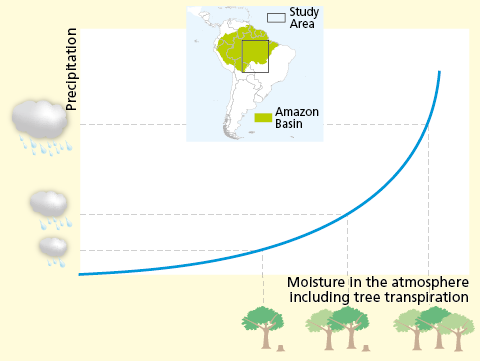
Amazzonia: la deforestazione riduce le piogge

Amazzonia: la deforestazione riduce le piogge

È stato presentato oggi, 9 agosto 2021, il Rapporto del Working Group I IPCC (International Panel on Climate Change) che valuta le ultime conoscenze scientifiche sul clima della Terra emerse rispetto al rapporto precedente del 2013.
The intensification of extreme weather events, coastal erosion and sea-level rise are major challenges to be urgently
addressed by European coastal cities. The science behind these disruptive phenomena is complex, and advancing climate
resilience requires progress in data acquisition, forecasting, and understanding of the potential risks and impacts for realscenario
interventions. The Ecosystem-Based Approach (EBA) supported by smart technologies has potential to increase
climate resilience of European coastal cities; however, it is not yet adequately understood and coordinated at European
level. SCORE outlines a co-creation strategy, developed via a network of 10 coastal city ‘living labs’ (CCLLs), to rapidly,
equitably and sustainably enhance coastal city climate resilience through EBAs and sophisticated digital technologies.
SCORE will establish an integrated coastal zone management framework for strengthening EBA and smart coastal city
policies, creating European leadership in coastal city climate change adaptation in line with The Paris Agreement. The
Coastal City Living Lab (CCLL) is a new concept that expands the Living Lab approach to coastal cities and settlements.
CCLLs will be set up to address specific climate challenges, and their effectiveness will be assessed by different
stakeholders through innovative monitoring systems and cutting-edge modelling approaches. SCORE will develop CCLLs in
a network of 10 cities which learn from each other in different frontrunner and follower roles. SCORE will involve citizen
science in providing prototype coastal city early-warning systems and will enable smart, instant monitoring and control of
climate resilience in European coastal cities through open, accessible spatial ‘digital twin’ tools. SCORE will provide
innovative platforms to empower stakeholders’ deployment of EBAs to increase climate resilience, business opportunities
and financial sustainability of coastal cities.
INDAGINI AMBIENTALI PER INDIVIDUAZIONE DELLA FALDA ACQUIFERA CHE INSISTE NELL'ARIA DEL-LA DISCARICA DI MELICUCCA' (RC) . VERRANNO SVOLTE INDAGINI DI TIPO METEOROLOGICO GEOFISICO0 E GEO-CHIMICO A CURA DEGLI ISTITUTO CNR ISAC E ISPC E ISAFOM. IL RISULTATO DELLE INDAGINI SARA' PROPEWDEUTICOI ALL'INDIVIDUAZIONE DEL RISCHIO DI CONTAMINAZIONE DELLA FALDA ACQUIFERA SOTTOSTANTE LA DISCARICA. L'INDAGINE DOVRA' DETERMINARE L'ESTENSIONE LA FORMA E IL CORPO IDRICO COMPLESSIVO STABILENDO LE CONDIZIONI DI PARTENZA IN TERMINI DI CONTAMINAZIONE DEL TOP-SOIL E DELLA PRECIPITAZIONE AL SUOLO INCLUSI LA CAPACITA' DI EVAPORAZIONE DEL SUOLO
Il progetto si colloca nell'ambito di un progetto H2020 denominato SINOPTICA già in atto e coordinato da CIMA. Il contributo che ISAC-CNR dovrà fornire consiste nella realizzazione dei quattro punti seguenti:
• un documento di progettazione degli esperimenti di assimilazione dei dati di fulminazione;
• una versione del modello meteorologico WRF, comprensivo del pacchetto di assimilazione fulmini, installato su macchine messe a disposizione dal progetto H2020 SINOPTICA;
• un manuale d'uso e di installazione;
• un rapporto di sintesi dei risultati degli esperimenti eseguiti.

ATMO-ACCESS (https://www.atmo-access.eu/) is the organized response of distributed atmospheric research facilities for developing a pilot for a new model of Integrating Activities. The project will deliver a series of recommendations for establishing a comprehensive and sustainable framework for access to distributed atmospheric Research Infrastructures (RI), ensuring integrated access to and optimised use of the services they provide. ATMO-ACCESS mobilizes extensive resources in the atmospheric RIs communities to engage into harmonizing access procedures in relation to policies, financial regulations and conditions for access. It will develop and test innovative modalities of access to facilities and complementary and more advanced services, including digital services, developed as part of cross-RI efforts. ATMO-ACCESS will open physical and remote access to 43 operational European atmospheric research facilities, including ground-based observation stations, simulation chambers, but also mobile facilities and central laboratories that are fundamental elements in distributed RIs.
The Monte Cimone – Po Valley facility (which encompasses the “O. Vittori” observatory at Monte Cimone and the measurement sites at Bologna and S. Pietro Capofiume, see https://atmo-access.isac.cnr.it/), managed by CNR-ISAC, is among the ground-based observation stations that will provide physical and remote access to external users.
*********
ATMO-ACCESS (https://www.atmo-access.eu/) rappresenta la risposta alla necessità di organizzare un nuovo modello di accesso ai servizi offerti dalle infrastrutture di ricerca atmosferica distribuite. Il progetto fornirà una serie di raccomandazioni per stabilire un quadro completo e sostenibile per l'accesso alle infrastrutture di ricerca atmosferiche distribuite (RI), garantendo l'accesso integrato e l'uso ottimizzato dei servizi che esse forniscono. ATMO-ACCESS mobilita vaste risorse nelle comunità delle RI atmosferiche per impegnarsi nell'armonizzazione delle procedure di accesso in relazione alle politiche, ai regolamenti finanziari ed alle condizioni di accesso. Svilupperà e sperimenterà modalità innovative di accesso alle infrastrutture ed ai servizi complementari, compresi i servizi digitali, sviluppati in un’ottica interdisciplinare. ATMO-ACCESS fornirà possibilità di accesso fisico e remoto a 43 strutture operative di ricerca atmosferica in Europa, comprese stazioni di osservazione a terra, camere di simulazione, ma anche strutture mobili e laboratori centrali che sono elementi fondamentali nelle RI distribuite.
La facility Monte Cimone – Po Valley (che comprende l'Osservatorio “O. Vittori” del Monte Cimone e i siti di misura di Bologna e S. Pietro Capofiume, vedi https://atmo-access.isac.cnr.it/), gestita del CNR-ISAC, è tra le stazioni di osservazione a terra che forniranno l'accesso fisico e remoto agli utenti esterni.
Verrà effettuata una calibrazione per confronto dei sensori costituenti la rete micrometeorologica di ARPA Lazio. Periodicamente, ogni strumento viene rimosso durante la manutenzione preventiva dal sito in cui normalmente opera, e viene consegnato al CNR-ISAC di Roma Tor Vergata. Presso questo sito viene sottoposto alla calibrazione, che consiste in un confronto sistematico e documentato con uno strumento campione (uno standard di trasferimento) di classe superiore. Al termine del periodo di calibrazione, il file contenente le misure relative allo standard di trasferimento ed al sensore da tarare verrà reso non modificabile e memorizzato in un opportuno archivio informatico. Seguirà una fase di elaborazione, che analizzerà le misure raccolte, verificherà che il sensore da tarare non abbia manifestato malfunzionamenti tali da richiedere il suo invio al produttore per controlli ulteriori e riparazioni, produrrà le elaborazioni per determinare sia l'incertezza intrinseca che, eventualmente, la curva di calibrazione, e preparerà la documentazione di corredo alla calibrazione stessa.
Tutte queste operazioni saranno completamente tracciabili, e seguiranno procedure operative standardizzate descritte in un apposito documento CNR-ISAC. Le relative procedure di elaborazione saranno documentate e realizzate da opportuni programmi di elaborazione, che verranno preventivamente trasmessi ad Arpa Lazio per la relativa approvazione. Il CNR-ISAC effettuerà tutte le calibrazioni richieste per confronto (salvo ove diversamente specificato), facendo riferimento prevalentemente agli standard internazionali fissati dallo ISO (International Organization for Standardization) e dal WMO (World Meteorological Organization).
C3S_511 Project provides a service that delivers robust and sustained Quality Assessments of all observational and reanalysis-based Essential Climate Variable products available via the Copernicus Climate Service Climate Data Store. C3S_511 service addresses all the tender needs, considering all prioritized ECVs coming from observations and reanalyses in all GCOS components (Atmosphere, Ocean, Land) within the planned service duration.
C3S_511 will address the wide-ranging technical and scientific requirements set out in the ECWF ITT by: (1) working adaptively to ensure continuity with functional outcomes of the CDS, (2) providing scientific evaluation employing state-of-the-art data analysis methodologies of a multi-thematic CDS, including comparisons with existing independent data, and (3) providing routine reappraisal of C3S CDRs.
C3S_511 squares the circle by providing robustly derived assessments of observational and reanalysis product quality in a manner that is interoperable with model based assessments to support effective use of the CDS. Our solution will unify approaches, procedures and outputs between observational and model quality assessments carried out in C3S.
The Erasmus+ Strategic Partnership “Cultural Heritage Protection in Climate Change online (CHePiCC online)” translates state-of-the-art research on climate change and cultural heritage protection into distance and blended learning programmes for HE learners, following EU guidelines and directives as well as firmly basing the preparedness approach for cultural heritage protection on the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. The main and longterm objective of this project is to bring heritage back into HE teaching and learning, to enable future generations to protect cultural heritage and thereby identity for the future and to facilitate a behavioural change concerning cultural heritage protection and climate change, especially in the future professional lives of HE learners and teachers. The necessary holistic approach to the wide topic of cultural heritage protection is ensured by the transdisciplinary composition of the partnership which holds expertise in cultural property protection, cultural landscapes, climatology and climate change, structural engineering, material handling, preparedness measures, heritage sciences, conservation-restoration and the collaboration with emergency responders. All partners bring state-of-the-art research from current high-profile research projects to the partnership and thus guarantee a research based approach to HE and with their individual expertise on distance and blended learning in HE a student centred approach in the developed outputs of the project.
CHePiCC online is firmly anchored within current European incentives to mitigate climate change and to protect cultural heritage which is an integral part of our identities and which is severely threatened by climate change and climate change induced natural disasters. Following the success of the European Year of Cultural Heritage in 2018, the European Framework for Action on Cultural Heritage names the holistic approach to the topic as one of the four principles for success and highlights the importance of cultural heritage as a resource for the future. The project’s main output, an open-access Massive Open Online Course on cultural heritage protection in climate change promotes cultural heritage as exactly that resource and enables higher education (HE) teachers and learners to build their future on our pasts. Cultural heritage is exposed to a number of risks in the 21st century, a fact that is highlighted by the joint EU-UNESCO Initiative#7 “Heritage at risk” as well as ICOMOS, which in 2019 put a focus on engaging cultural heritage in climate action and a number of high-profile research project programmes funded by the EU.
The partnership CHePiCC online consists of four universities – one from Northern Europe (NTNU), two from Central Europe (DUK, UAA) and one from the most Southern Europe (ULPGC) – and two renowned research institutes based in Italy (CNR-ISAC) and the Czech Republic (ITAM). The partners hold complementary expertise on cultural heritage protection, cultural landscapes (in particular on the types of cultural landscapes of their specific climate zones), climate change, maintenance, structural and material engineering,
material handling and HE e-learning in distance and blended formats.
The immediately tangible objectives of the project are a) a Massive Open Online Course on Cultural Heritage Protection in Climate Change (covering cultural landscapes, built heritage, material preservation and climate change and thus create an interconnection between the topics), b) a tested and evaluated concept for a transdisciplinary summer university on cultural landscapes in climate change and c) a tested and evaluated concept for a live exercise in cultural heritage protection which requests the close cooperation of a number of academic disciplines and emergency responders, thus reflecting immediately the multi-stakeholder based cooperation needed in cultural heritage protection and climate change.
Due to the nature of the CHePiCC online outputs they reach every one with a functioning internet connection, and are available and accessible also for HE students and teachers or other interested groups who face geographical, social or economic obstacles or have physical limitations which hamper their mobility. Thus the outputs of CHePiCC online are highly inclusive and tackle skill gaps and mismatches in HE with a topic that is one of the high priorities in the 21st century. All developed HE teaching and learning material is highly adaptable and available for free for inclusion into any HE curriculum of every related subject, thus supporting the overall goal of the CHePiCC, to facilitate a behavioral change concerning cultural heritage protection in climate change by enabling HE students and with them future professional generations to build their future on our common past.